
Building an Industrial Effluent Treatment System
With the aim to provide a full picture on how the Malaysian government assures the industry to comply fully with the wastewater regulatory compliance, a webinar titled “Wastewater Regulation Compliance in Malaysia” was organised by UTAR Division of Community and International Networking (DCInterNet) on 18 July 2020 via zoom.
The talk was conducted by Technical & Innovative General Manager of I-Chem Solution Group Dr Thomas Wun and moderated by DCInterNet Director Assoc Prof Dr Lai Soon Onn. With extensive experience as a consultant in commissioning raw water treatment system, boiler water treatment system, cooling water treatment system as well as a wastewater treatment system, Dr Wun shared his experience of managing procedures and paperwork pertaining to the compliance of wastewater regulation according to Environmental Quality Act 1974 (Act).
According to him, his responsibility involved dealing with the Department of Environment (DOE) on behalf of the wastewater plant management. He also provided a brief introduction on Environmental Regulation and interpreted some terms.
“Industrial Effluent Treatment System (IETS) refers to any facility including the effluent collection system, designed and also constructed for the purpose of reducing the potential of industrial effluent or mixed effluent that causes pollution,” explained Dr Wun.

Dr Wun during the webinar

All the wastewater plants have to comply with the wastewater regulation according to the Environmental Quality Act 1974 (Act)

Dr Wun showing the categories of wastewater
“Before the design and the construction of IETS, we have a ‘Pre IETS Design and Construction Regulation’. The first thing to do is to figure out the category of the wastewater according to the characteristic listed on the Environmental Quality (Scheduled Waste 2005),” said Dr Wun.

Generally, two processes are involved in the IETS. The influent (wastewater) has to first go through a process called Physical Chemical Process (PCP) which contains EQ Tank, Coagulation/Flocculation and DAF/Clarifier. The second process of water purification is called the Biological Process (BP). It contains Aeration Tank and Secondary Clarifier. The influent will then recycle the BP process and the sludge will be sent to the Primary Sludge WAS.
“Each wastewater plant may have different IETS process. The process shown in the chart is just a general flow,” said Dr Wun.
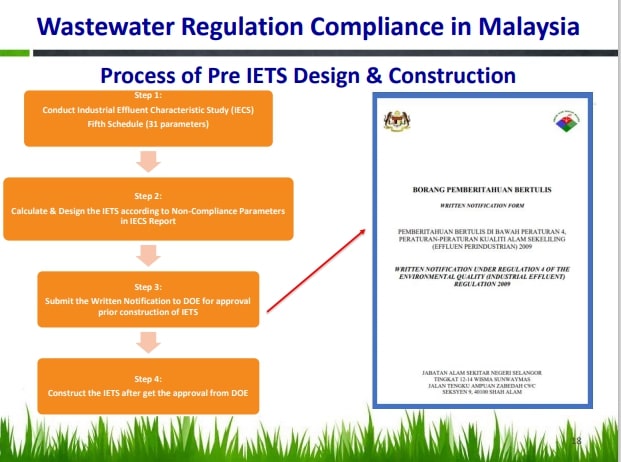
The process of Pre IETS Design and Construction
“The calculations and designs of IETS are done according to non-compliance parameters in the IECS Report. If the design does not fulfil the guidelines written in the “Guidance Document on the Design and Operation of Industrial Effluent Treatment Systems”, the DOE will not approve the treatment system.”
After all the calculations and designs are settled, the wastewater plant needs to submit a written notification (Borang Pemberitahuan Bertulis) to the DOE for approval before the IETS construction begins. The written notification form can be downloaded at the DOE website.
“If the information provided by the wastewater plant is incorrect, the DOE will ask us to amend the written notification. Sometimes, our customers take a few months to get the approval of a written notification (Borang Pemberitahuan Bertulis) from the DOE,” he said and added, “The IETS can only be constructed after the factory gets the approval.”
After the IETS has been constructed and tested, the factories will have another regulation to comply, namely “Post IETS Design and Construction Regulation”.

Dr Wun explaining “Post IETS Design and Construction Regulation”
In 2016, the DOE introduced Guided Self-Regulation (GSR), a self-regulated enforcement that allows factories to guide the regulation themselves. In order to make sure all the wastewater plants implemented the GSR, the DOE sent officers to check whether the factories complied with all the regulations. According to the GSR, the wastewater plants need to look out for eight components, namely Environment Policy, Competent Person, Environment Management and Decision Making Process Committee, Performance Monitoring Facilities and Instruments, Record Keeping, Data Analysis and Interpretation, Reporting and Communication as well as the Continuous Improvement.

The eight components of Guided Self-Regulation (GSR)
“The Environment Management Committee is separated into two groups. The Environmental Performance Monitoring Committee (EPMC) is made up of senior officers who are in charge of maintenance and performance pollution control system (PCS) at the operational level. On the other hand, the Environmental Regulatory Compliance Monitoring Committee (ERCMC) consists of general managers and CEOs who are policymakers,” said Dr Wun.
Dr Wun also presented the examples of “Record Keeping” and “Data Analysis & Interpretation” required by DOE according to Regulation 27.
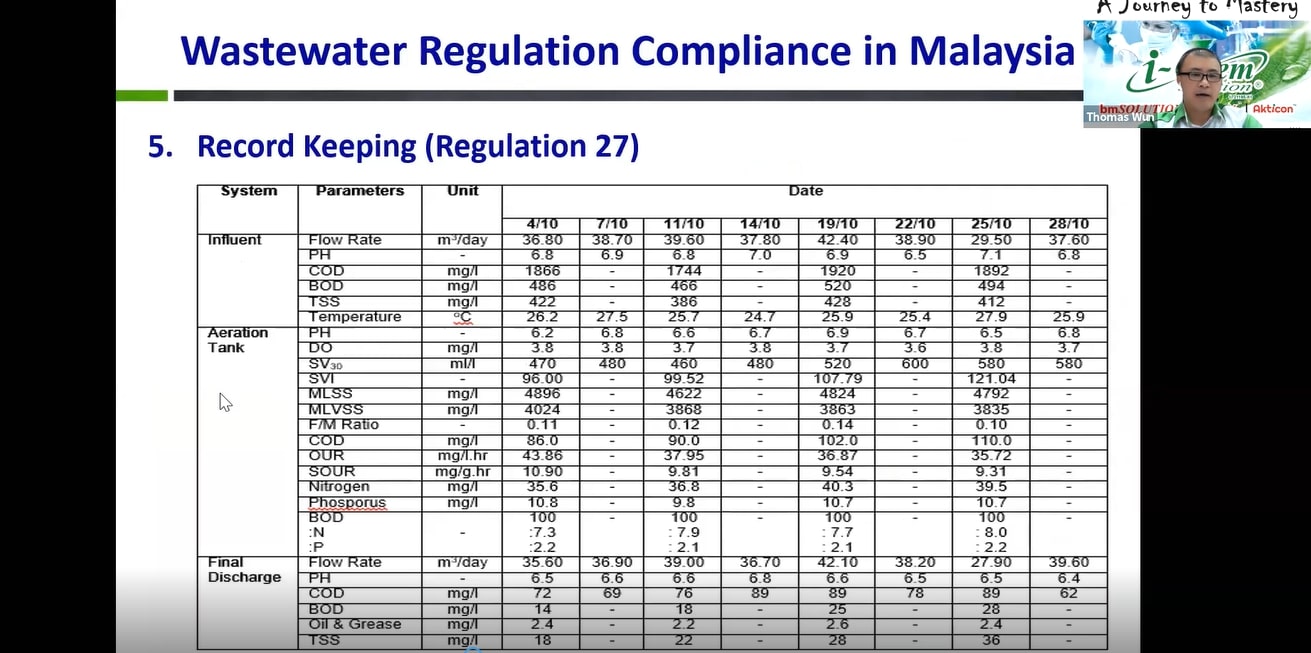
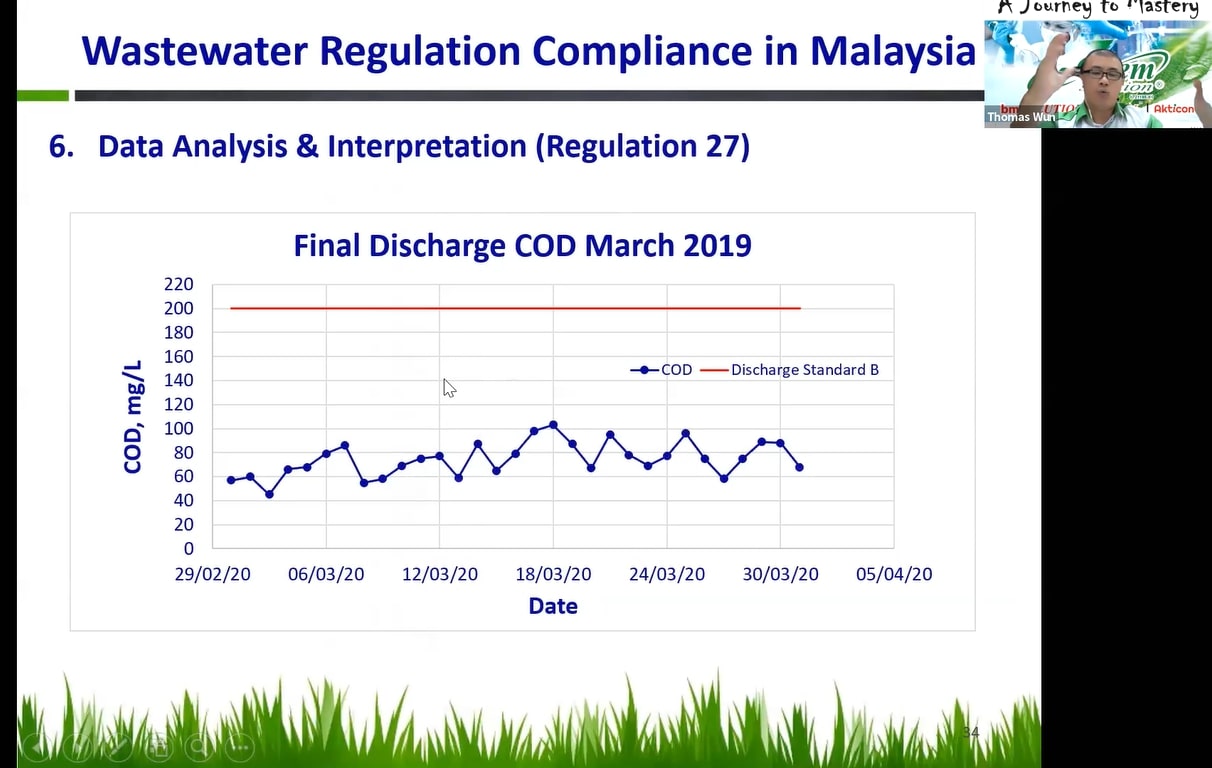
Dr Wun presenting “Record Keeping” (left) and “Data Analysis & Interpretation” (right) stated under Regulation 27
The “Reporting & Communication” (Regulation 7) is done monthly via the submission of reports using Jabatan Alam Sekitar dan Air website (oer.doe.gov.my).
At the end of the talk, Dr Wun displayed some non-compliance examples in the industry, showing what the DOE will do if they found the factory did not comply with the wastewater regulation completely. According to him, the DOE officer will send a “Field Citation” to the factory. The “Field Citation” form points out the regulation that has not been complied by the factory. Subsequently, the factory will receive a DOE Order Notification (Notis Arahan). The DOE Order Notification states the regulation that has been failed to be complied by the factory, as well as the remedial action that should be taken immediately by the factory to reduce water pollution. The factory is then required to send a reply letter to the DOE and pay the compound (penalty) stated in the official letter.
“Legal action will be taken by the government if the factory failed to comply with the Order Notification. The factory, however, can write a letter to appeal for a lower amount of penalty,” said Dr Wun, adding “My job is to help the industrial factories deal with the regulation matter.”
The webinar ended with a Q&A session and a group photograph.

The “Field Citation” will be sent by the DOE after a visitation from the DOE officer

The first part of DOE Order Notification (Notis Arahan)

The second part of DOE Order Notification (Notis Arahan): Non-Compliance Regulation

The third part of DOE Order Notification (Notis Arahan): Remedy Action that can be done by the factory

A factory needs to write a reply letter to DOE within a period of time
Dr Wun (top left) with other participants
![]()
![]()
© 2020 UNIVERSITI TUNKU ABDUL RAHMAN DU012(A).
Wholly owned by UTAR Education Foundation Co. No. 578227-M LEGAL STATEMENT TERM OF USAGE PRIVACY NOTICE