
Dr Lee (top row, most left) during the sharing session
Blockchain is an emerging application based on
distributed computing and cryptography. Bitcoin is one of the most
well-known applications of blockchain technology which revolutionised the
development of crypto-currency. Blockchain 2.0 has impacted various
industries including finance (FinTech), manufacturing, insurance and
renewable energy (SolarCoin).
Thus, to enlighten the academics of
UTAR and the members of the public on
blockchain technology as well as its development and applications, the
Centre for Curriculum Development and Innovation (CCDI) organised a webinar
titled “Introduction to Blockchain Technology and Overview of its
Applications” on 30 October 2020 via Microsoft Teams.
The speaker for the sharing session was Gachon
University, South Korea researcher Dr Lee Wai Kong. He has vast experience
in R&D as a reviewer for various international journals such as Institute of
Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Transactions on Dependable and
Secure Computing (2016 & 2017), IEEE Sensors, IEEE Internet of Things
Journal (2018-2020) and IEEE Transactions on Industrials Informatics
(2018-2020).
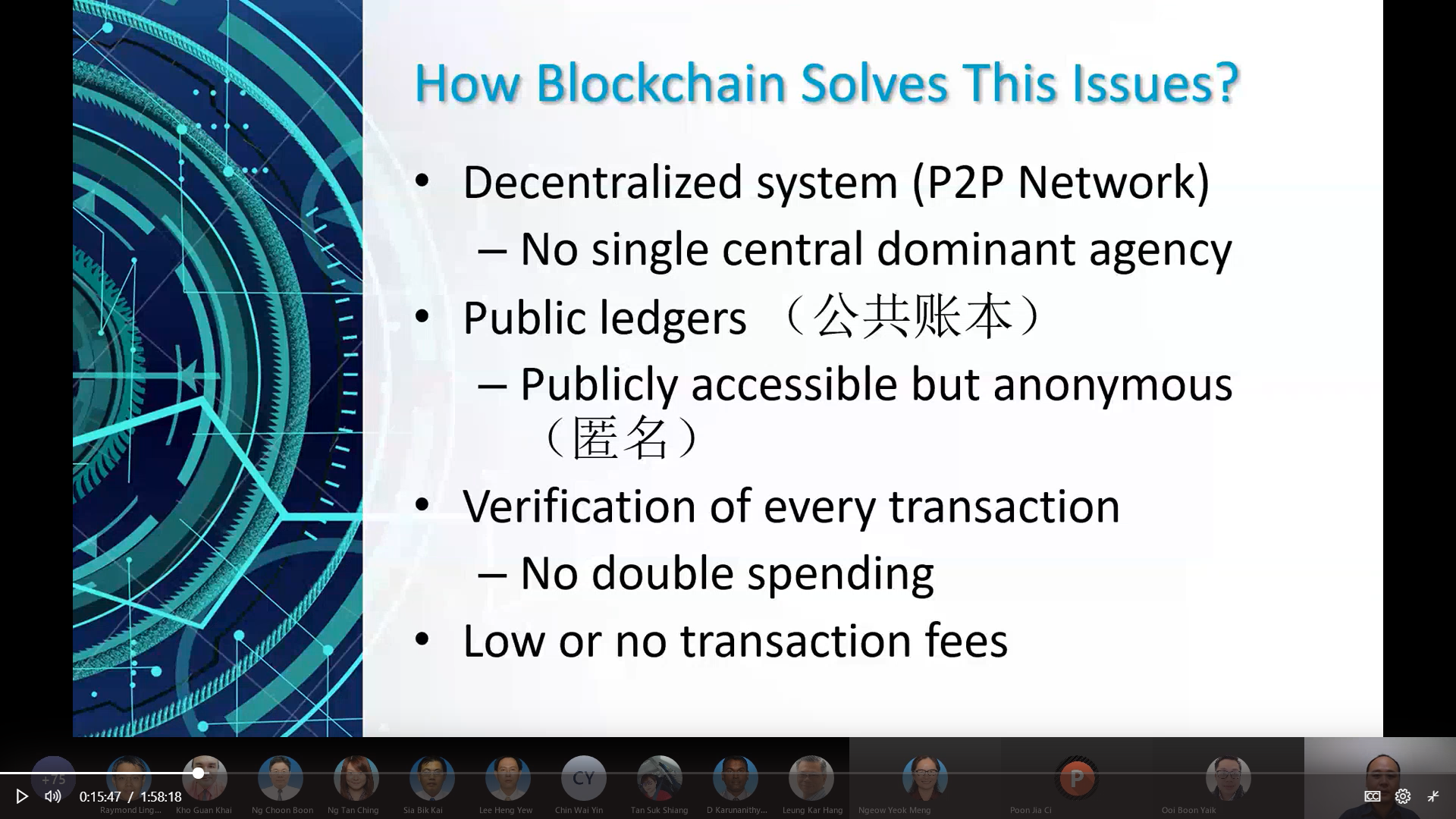
Dr Lee explaining how blockchain
technology solves the motivations
Dr Lee first explained the reason why blockchain
technology appeared, “In the beginning, bitcoin and blockchain technology
were used interchangeably. So when people say blockchain technology, it is
usually referring to Bitcoin and vice versa. Another reason is because
people are finding ways to replace the current currency system. There are
four motivations of blockchain technology; it involves high transaction fees
by trusted third party, double spending, net frauds and account hacking, and
financial crisis and crashes.”
Dr Lee then introduced the audience to secret and
public key cryptography, “There are two types of keys which are Secret Key
Cryptography and Public Key Cryptography. Secret Key Cryptography involved
communicating parties that share the same private key. The person can
encrypt and decrypt digital data by the same given message and the same key.
Public Key Cryptography involved communicating parties that use different
keys. In Public Key Cryptography, many people can potentially obtain the
encrypted data, but only the person with the secret key can decrypt the
message.”


Dr Lee presenting the difference
between Secret Key Cryptography and Public Key Cryptography
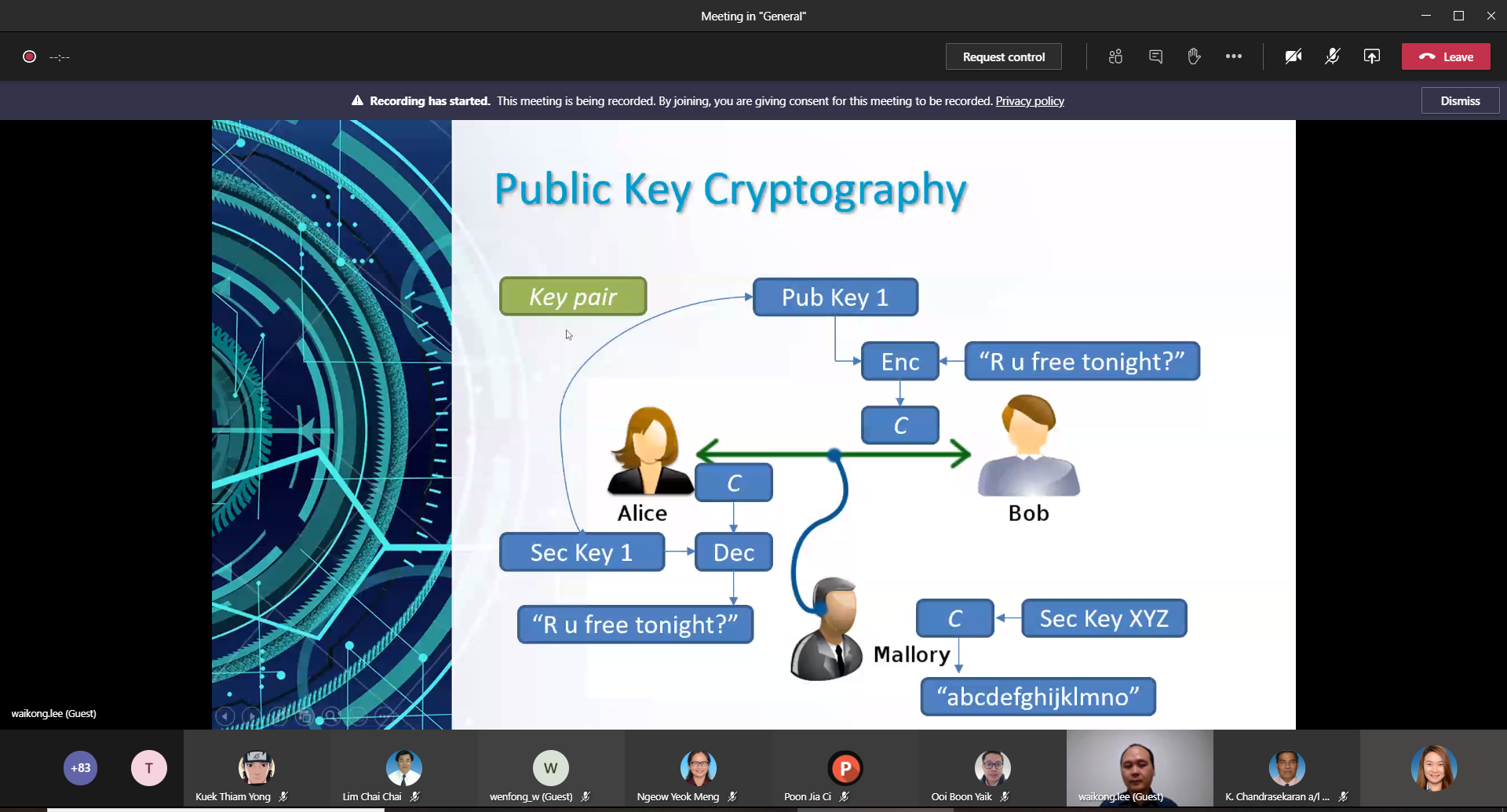
Dr Lee showing the example of public key cryptography


Advantages and disadvantages of
Bitcoin
Dr Lee later spoke about the advantages and
disadvantages of Bitcoin, “Bitcoin is cryptographically secured as
authentication is needed to publicly verify the transactions. Everyone that
has access to the network can verify the transaction. The system is very
secure, if anyone wishes to break into the system, you need more than 51% of
malicious nodes to break it.”
“On the other hand, Bitcoin also has its limitations.
The finance transaction is rather slow in this high-speed transaction world;
it takes tens of minutes to complete a transaction. There is also a huge
amount of memory involved to store the public ledger. And the most debatable
problem is the difficulty to trace the real user’s identity; this will
encourage more illegal activities like money laundering and ransomware,” he
added.
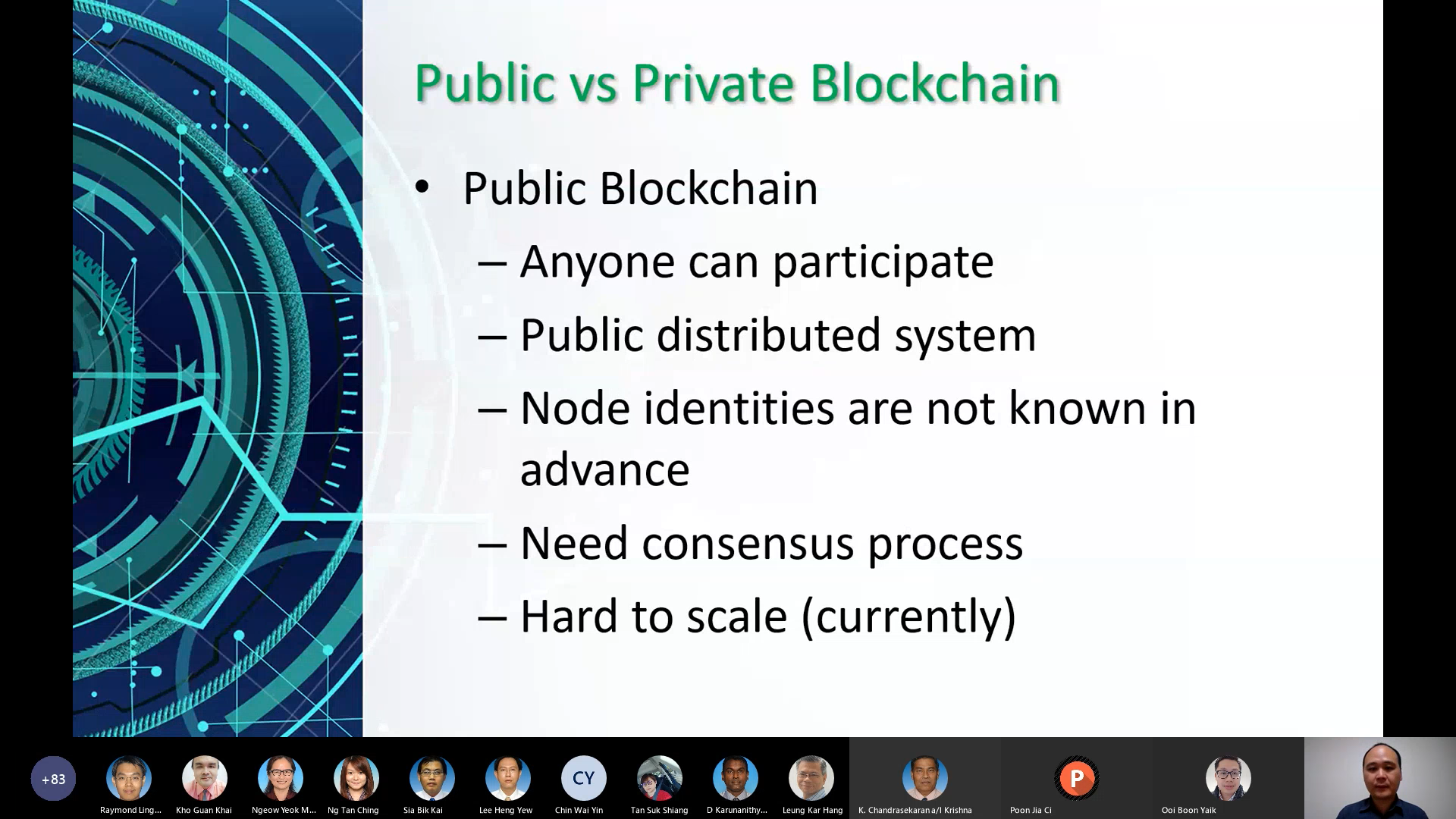
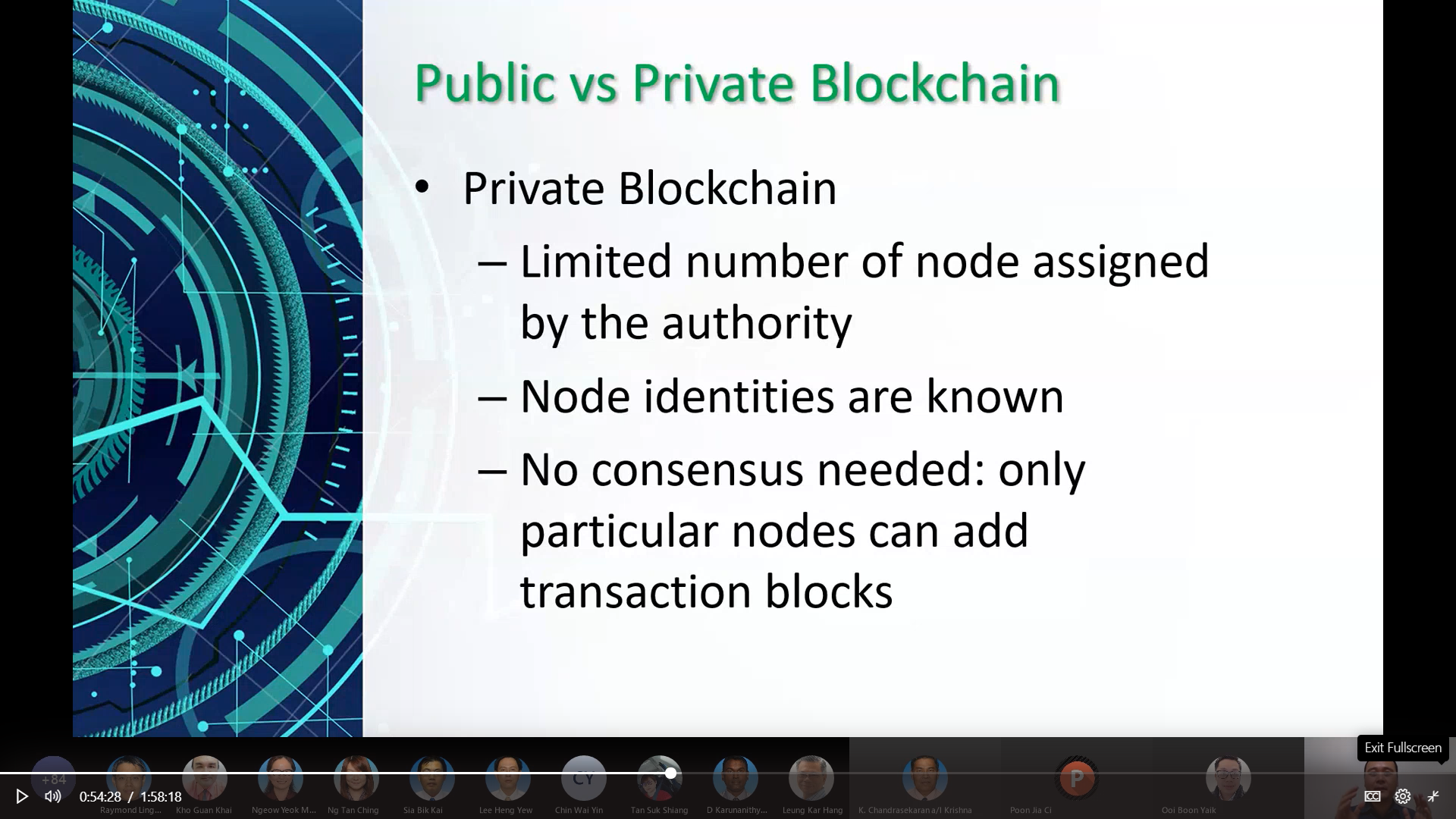
Dr Lee introducing the concept of
public and private blockchain
Dr Lee then moved on to explain the idea of smart
contracts, “The advancement of technology from blockchain 1.0 to 2.0 made
people come up with another idea about cryptocurrency. They are thinking of
ways to use technology to do other things, for example, exchanging data
instead of money. Hence, the idea of smart contracts was introduced. Smart
contracts involved data transaction; it is a digital data that can be either
partially or fully executed without human interaction. It can be used to
execute some agreed job automatically.”

Blockchain 2.0 Smart Contracts allow
more applications and can trade more things compared to Blockchain 1.0
He then further explained the current blockchain,
“The current blockchain is now interconnected and is called Blockchain 3.0.
Blockchain 3.0 is like the Internet; it links a group of different
blockchain networks through the smart contract. In blockchain 3.0, the
different types of blockchain can communicate and exchange data.”
Dr Lee also discussed two case studies, namely,
“Enabling Localised Peer-to-Peer Electricity Trading Among Plug-in Hybrid
Electric Vehicles Using Consortium Blockchains” and “MeDShare: Trust-Less
Medical Data Sharing among Cloud Service Providers via Blockchain” with the
participants.
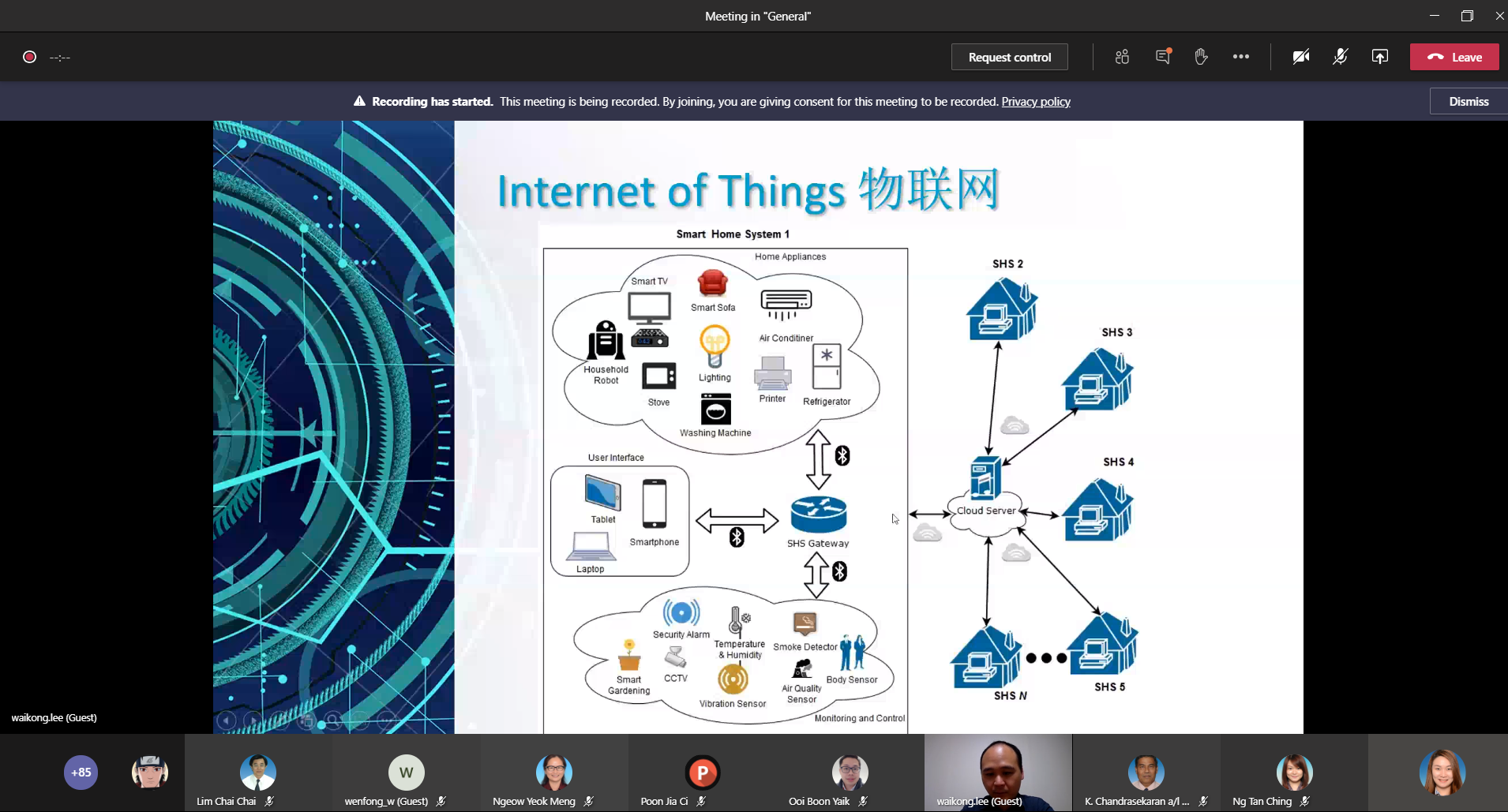
Blockchain in our future life – the smart home system
Dr Lee concluded his sharing session by giving advice
to the participants, “Blockchain is an emerging and relatively new
technology, but it is not meant for every application. Although blockchain
is very innovative and creative, the maintenance cost for blockchain could
be high especially for the public blockchain. Ask yourself, do you really
need it? I will advise you to think carefully before having it.”
The sharing saw an active interaction between the
speaker and the participants. The insightful talk ended with an equally
interesting Q&A session.
![]()
Wholly owned by UTAR Education Foundation Co. No. 578227-M LEGAL STATEMENT TERM OF USAGE PRIVACY NOTICE