
Virtual talk focuses on IoT technology in the 21st century
Dr Goh introducing the Industry 4.0 concept as well as its current and future developments
UTAR Department of Soft Skills Competency (DSSC) of Kampar Campus organised a virtual talk titled “Towards Industrial Revolution 4.0 (Industry 4.0): Starting from IoT technology to assist 21st century industry” (朝向工业4.0: 从IoT科技开始,辅助21世纪工业) on 13 January 2021 via Zoom.
The webinar was conducted by UTAR Faculty of Information and Communication Technology (FICT) Deputy Dean for R&D and Postgraduate Programmes Ts Dr Goh Hock Guan. It saw more than 300 participants consisting of students, staff and public members.
Dr Goh is also a public lecturer for the topic Industrial Revolution 4.0 in Malaysia. His areas of expertise are agriculture monitoring system, cognitive wireless sensor network, environmental monitoring system, internet of things (IoT), mobile networking and wireless communications. He had served as an information and communication technology consultant for companies previously.
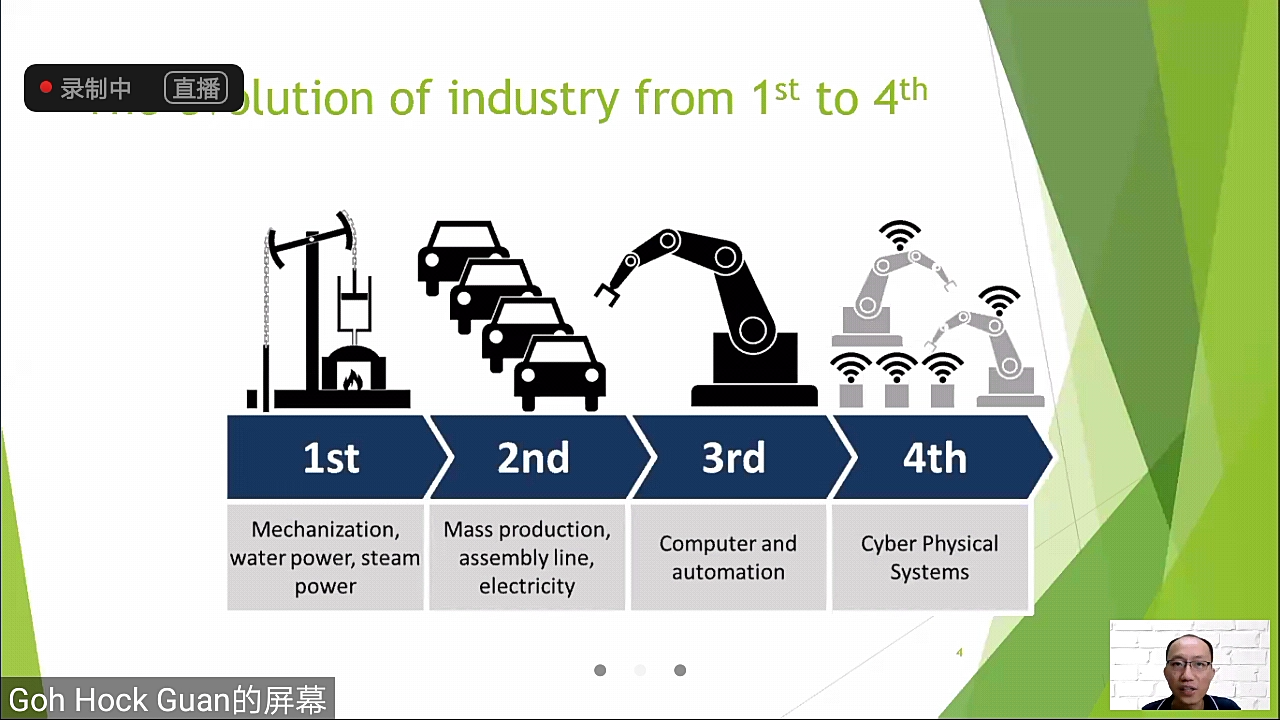
Dr Goh explaining the revolution of industry from Industry 1.0 to Industry 4.0
He first gave a brief introduction on the revolution of industry from Industry 1.0 to Industry 4.0 and explained, “Industry 1.0 focuses on mechanisation, water power and steam power; Industry 2.0 focuses on mass production, assembly line and electricity; Industry 3.0 focuses on computer and automation while Industry 4.0 focuses on cyber-physical systems.”
He then elaborated on the concept and framework of Industry 4.0 and said, “It started with the term INDUSTRIE 4.0 in the year 2010 by the German government. These cyber-physical systems were comprised of smart machines, storage systems and production facilities capable of autonomously exchanging information, triggering actions and controlling each other independently. This facilitates fundamental improvements to the industrial processes involved in manufacturing, engineering, material usage and supply chain. The important elements in Industry 4.0 are integration, analytics, cyber security and transformation.”
“Industry 4.0 makes things ‘smart’. Nowadays, we have smart manufacturing, smart warehouse, smart transportation, smart farm, smart waste management and many more. It can be predicted that by the year 2030, Industry 4.0 will focus on artificial intelligence (IoT+5G=AI), genetic engineering, new materials such as carbon-based materials - superconductors to replace silicon, quantum technology, and nuclear fusion to produce clean and cheap energy,” he added.
According to him, various Industry 4.0 initiatives have been initiated around the world, such as “Industry 4WRD” by Malaysia, “Smart Manufacturing” by the United States, “Made in China 2025” by China, “Industrial Value Chain Initiative” by Japan and “Smart Nation Programme” by Singapore.
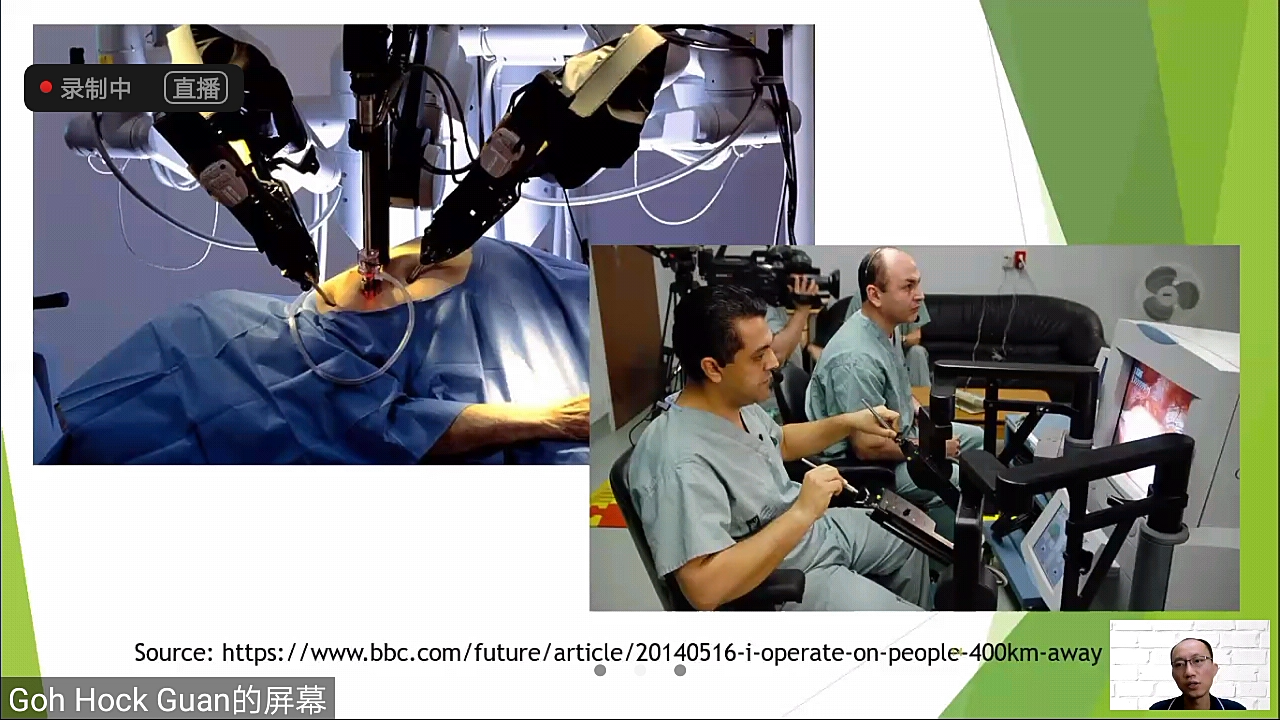
IoT creates surprising value in healthcare which enables doctors to do remote surgery on patients from 400km away
By using real-life examples, he elaborated on the technologies involved in Industry 4.0 which included digitisation, IoT, cloud computing, big data, AI, machine-to-machine (M2M), human-machine interfaces, blockchain, software defined technologies, cybersecurity, augmented reality, autonomous robots, additive manufacturing, smart grid, and intelligent transportation, and how these technologies play an important role in the Covid-19 pandemic.

Industry 4.0 technologies play an important role in the Covid-19 pandemic
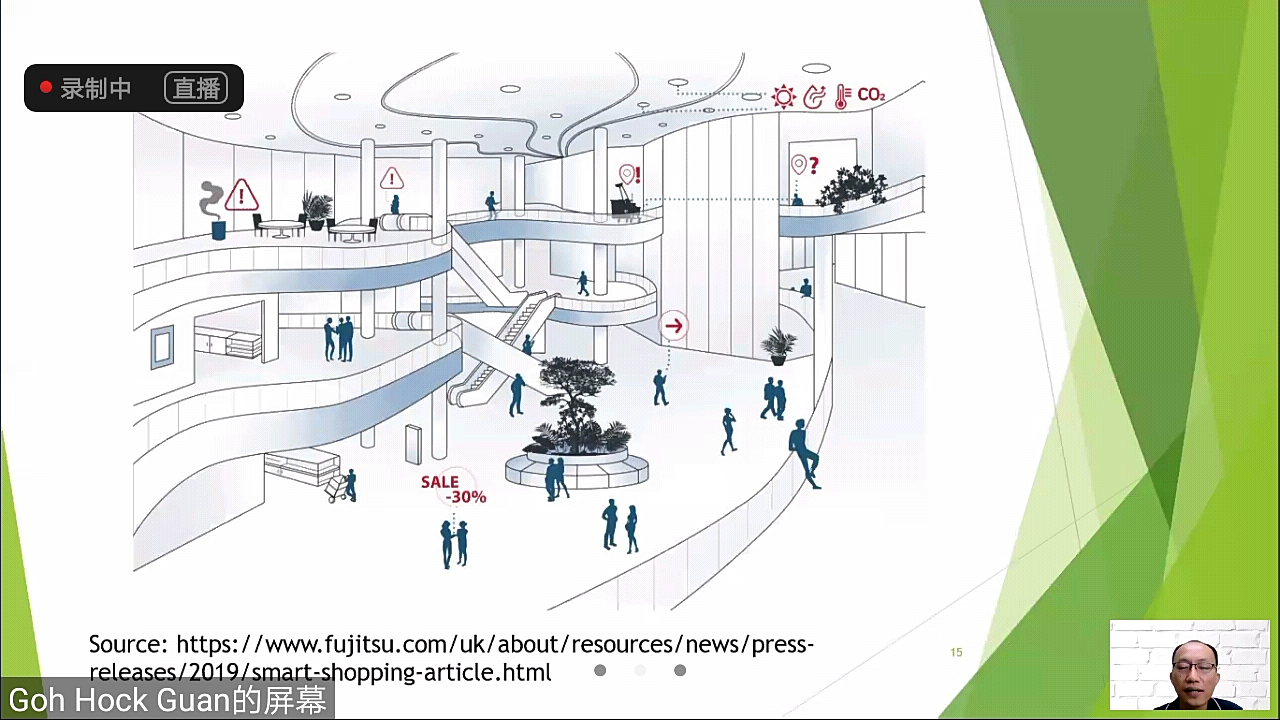
IoT to enhance customer experience in shopping centres in the “smart-shopping system”
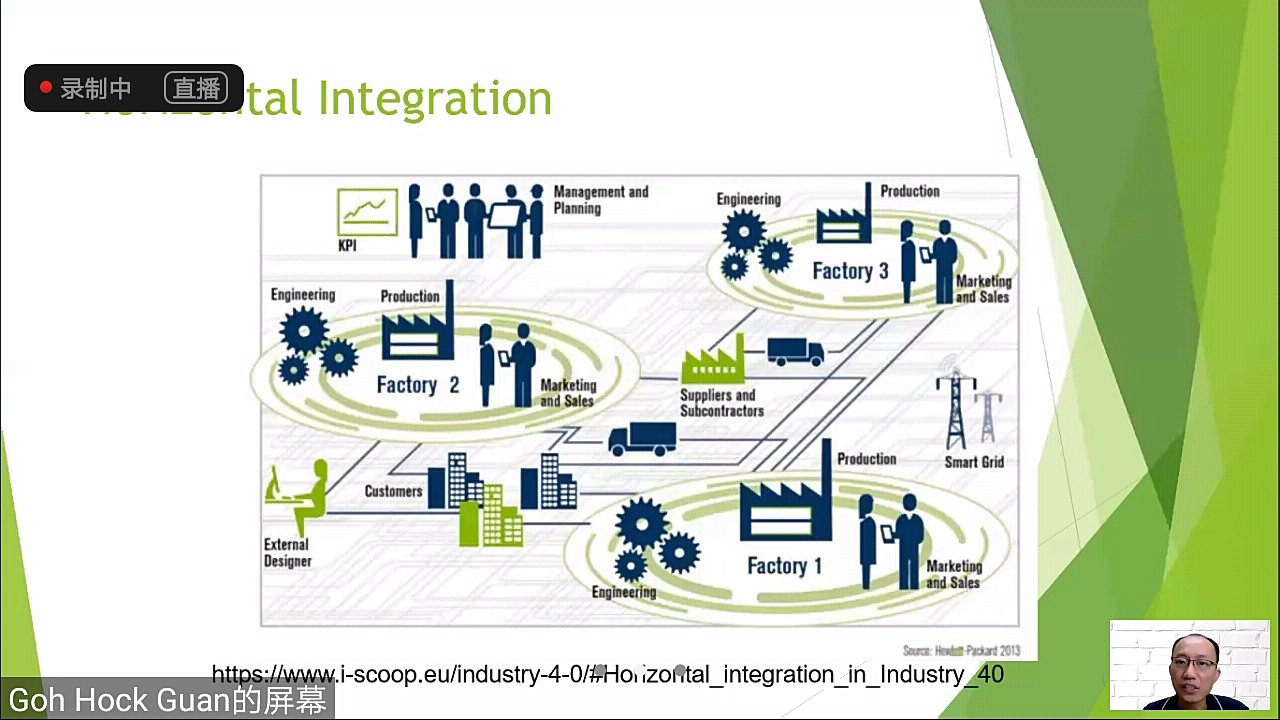
Industry 4.0 encourages horizontal integration
During the Q&A session, Dr Goh discussed topics related to automatic anomaly detection, quantum technology, and technical and personal skills for Industry 4.0, to name a few.
![]()
© 2021 UNIVERSITI TUNKU ABDUL RAHMAN DU012(A).
Wholly owned by UTAR Education Foundation Co. No. 578227-M LEGAL STATEMENT TERM OF USAGE PRIVACY NOTICE